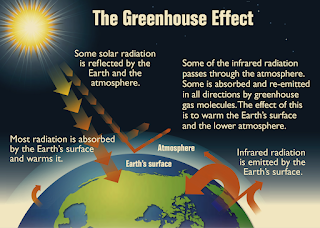
The greenhouse effect is a phenomenon where Earth's atmosphere traps the Sun's heat, resulting in warmer temperatures and it is a key factor in making Earth a comfortable place to live.
The greenhouse effect operates similarly to a greenhouse, a glass-walled building used to grow plants like tomatoes and tropical flowers, resembling the process of growing in a greenhouse.
The primary greenhouse gases are carbon dioxide, methane, water, nitrogen oxide, ozone, and chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs).
A greenhouse maintains warmth inside during winter by allowing sunlight to warm plants and air, and trapping Sun's heat through its glass walls, despite the colder outside temperatures.
The greenhouse effect on Earth occurs when greenhouse gases, like carbon dioxide, trap heat like a greenhouse's glass roof.
The Sun's sunlight warms Earth's surface, while its surface cools at night, releasing heat back into the air. Some of this heat is trapped by greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, keeping Earth's average temperature at 58 degrees Fahrenheit.
Importance of Greenhouse effect for life on earth
Green house effect is necessary for life because Without any greenhouse gases, Earth would be an icy wasteland. Greenhouse gases keep our planet livable by holding onto some of Earth's heat energy so that it doesn't all escape into space.
A greenhouse is a safe haven for plants. It reduces the accessibility of insects and animals that have the potential to damage or destroy your plants. This greenhouse environment reduces exposure to extreme weather conditions such as torrential rain and droughts.
Greenhouse gases (also known as GHGs) are gases in the earth's atmosphere that trap heat. During the day, the sun shines through the atmosphere, warming the earth's surface. At night the earth's surface cools, releasing heat back into the air. But some of the heat is trapped by the greenhouse gases in the atmosphere.
The greenhouse effect significantly impacts Earth's average surface temperature, which is around 15°C, compared to 255 Kelvin or -18°C or 0°F without it. This would cause water on Earth to freeze, preventing life as we know it.
Earth's greenhouse gases, including carbon dioxide, methane, ozone, CFCs, and water vapor, are essential for maintaining Earth's temperature and life sustenance. These gases absorb solar energy, heating the atmosphere and causing the absorption of radiation. Without them, Earth's average temperature would decrease drastically, making it uninhabitable and making life impossible.
Causes of Greenhouse Effect
The major causes of Greenhouse effect are:
Burning of Fossil fuels
Fossil fuels are crucial for transportation and electricity production, but their burning releases carbon dioxide. As population increases, the utilization of these fuels increases, resulting in an increase in greenhouse gas emissions in the atmosphere.
Deforestation
Tree cutting leads to a significant increase in greenhouse gases, thereby causing a rise in Earth's temperature.
Farming
Nitrous oxide, a chemical found in fertilizers, is a significant contributor to the greenhouse effect in the atmosphere.
Industrial Waste and Landfills
Industries and factories emit harmful gases into the atmosphere, while landfills release carbon dioxide and methane, contributing to the increase in greenhouse gases.
Effects of Greenhouse effect
The main effects of Greenhouse effect are:
Global warming
The Earth's average temperature is gradually rising due to the release of greenhouse gases like carbon dioxide and methane from fossil fuel burning, vehicle emissions, industries, and human activities, causing environmental issues.
Ozone layer depletion
The ozone layer, located in the upper stratosphere, shields Earth from harmful ultraviolet rays from the sun. Depletion of this layer can lead to skin cancer and drastic climate changes, posing a significant threat to the planet.
The primary cause of this phenomenon is the rise in natural greenhouse gases such as chlorofluorocarbons, carbon dioxide, and methane.
Air pollution and smog
Smog is a mixture of smoke and fog, resulting from both natural and man-made factors.
Smog is formed by the accumulation of greenhouse gases like nitrogen and sulfur oxides, primarily from automobile and industrial emissions, agricultural fires, natural forest fires, and chemical reactions among themselves.
Water bodies Acidification
The rise in greenhouse gases in the air has caused the majority of the world's water bodies to become acidic. These gases combine with rainwater, forming acid rain, which then carries contaminants into rivers, streams, and lakes, further causing their acidification.
The phenomenon occurs when Earth absorbs more radiation than it can radiate back, reducing heat loss and increasing temperature. It is believed to have occurred on Venus' surface billions of years ago.
A runaway greenhouse effect occurs when a planet's temperature reaches the boiling point of water, converting ocean water into water vapor. This traps more sun-generated heat, increasing the planet's temperature and accelerating the greenhouse effect, also known as the "positive feedback loop."
The runaway greenhouse effect occurs when temperature rise due to various causes exceeds a certain threshold, leading to chemical reactions that release carbon dioxide from rocks into the atmosphere. This heats the planet's surface, accelerating the transfer of carbon dioxide from rocks to the atmosphere, resulting in the runaway greenhouse effect.
Climate change and Greenhouse effect
Global temperatures can significantly increase, with glaciers and ice caps melting faster than usual, causing sea levels to rise as meltwater drains into the oceans.
Glaciers and ice caps, covering 10% of the world's landmasses and holding 70%-75% of freshwater, could cause sea levels to rise by 70 meters if all ice is melted.
The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change reports a 1.8 millimeters per year increase in global sea level from 1961 to 1993 and a 3.1 millimeters per year increase since 1993.
Rising sea levels are causing flooding in coastal cities, potentially displacing millions of people in low-lying areas like Bangladesh, Florida, and the Netherlands.
Millions in Bolivia, Peru, and India rely on glacial meltwater for drinking, irrigation, and hydroelectric power, and its rapid loss could severely impact these nations.
Greenhouse gas emissions not only impact temperature but also alter precipitation like rain and snow.
Precipitation increased in eastern North and South America, northern Europe, and central Asia during the 20th century, while decreasing in Africa, the Mediterranean, and southern Asia.
Climate change threatens living habitats, posing threats to animals adapted to specific climates. Human societies depend on predictable rain patterns for food, clothing, and trade. If climate changes, these crops may be lost, and tropical diseases may expand into temperate regions. Scientists also worry that tropical diseases may expand their ranges in areas with higher temperatures.
Climate scientists unanimously agree that reducing greenhouse gas emissions is crucial, and various methods can be employed to achieve this goal:
The recommended actions include reducing driving, utilizing public transportation, carpooling, walking, or cycling.
The reduction in air travel is a significant step towards reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
Planting trees helps absorb carbon dioxide, reducing its release into the atmosphere.
Consuming less meat is crucial as cows are a significant producer of methane.
The focus is on promoting the use of alternative energy sources that do not rely on fossil fuels.
Use less electricity.
Conclusion:
The greenhouse effect makes the earth much warmer than without the atmosphere. In the form of heat, it consumes infrared radiation from the sun, which is lost to space after circulating in the atmosphere. The trees and plants take carbon dioxide, and in exchange, they release oxygen.